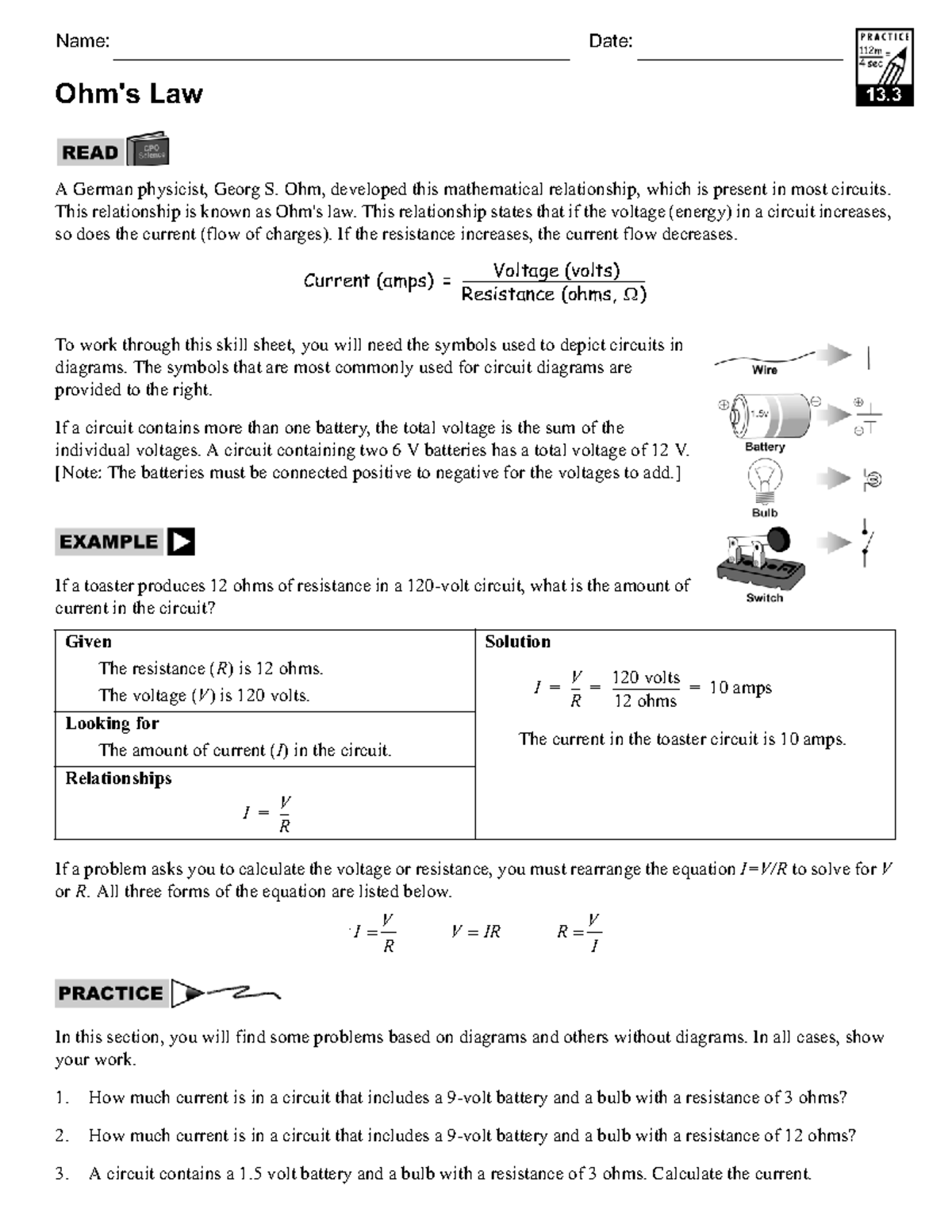
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in the field of electricity and electronics. It states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
One of the best ways to understand and apply Ohm’s Law is through practice worksheets. These worksheets typically involve solving for current, voltage, or resistance in various circuits using the formula I = V/R.
Example Problems
Let’s take a look at some example problems that you might encounter in an Ohm’s Law practice worksheet:
1. Calculate the current flowing through a resistor with a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms.
2. Determine the voltage across a resistor with a current of 2 amperes and a resistance of 8 ohms.
3. Find the resistance of a circuit with a current of 0.5 amperes and a voltage of 6 volts.
4. Solve for the current in a circuit with a voltage of 24 volts and a resistance of 12 ohms.
5. Calculate the voltage in a circuit with a current of 3 amperes and a resistance of 5 ohms.
By practicing these types of problems, you can improve your understanding of Ohm’s Law and gain confidence in solving electrical circuit calculations.
Remember, Ohm’s Law is a powerful tool that is used extensively in the field of electronics and electrical engineering. Mastering its principles can help you troubleshoot circuits, design new systems, and analyze the performance of existing devices.
Closing Thoughts
In conclusion, Ohm’s Law practice worksheets are a valuable resource for anyone studying electrical circuits. By working through problems and applying the formula I = V/R, you can enhance your skills and knowledge in the field of electronics. So, don’t hesitate to tackle those practice worksheets and test your understanding of Ohm’s Law!